SLAP is an acronym that stands for 'Superior Labral tear from Anterior to Posterior'. Figure 2. Surgery may be required if the tear gets worse or does not improve after physical therapy. 11 ). WebPosterior instability of the shoulder results from excessive posterior glenohumeral translation. The treatment options for posterior instability should be guided by the underlying pathology. Modern imaging techniques, in particular MRI, have greatly increased our ability to accurately diagnose posterior glenohumeral instability, and accurate recognition and characterization of the relevant abnormalities are critical for proper diagnosis and patient management.5, Multiple shoulder structures are important in resisting shoulder instability. The ligaments also help prevent the shoulder from dislocating. Normal shoulder MRI. Images of another patient with a posterior dislocation. The negative impact that posterior labral injuries have on a combine participants early NFL performance is important to consider especially because of how often these injuries occur among elite football players. Smith T, Drew B, Toms A. Reading time: 18 minutes. Posterior dislocations are uncommon and not as obvious on the X-rays as an anterior dislocation. Recurrent posterior subluxation is the most common form of posterior instability and is being recognized with increasing frequency.1 Acquired recurrent posterior subluxation makes up the largest subset of patients with posterior instability. The results of these tests will help your doctor decide if additional testing or imaging of your shoulder is necessary. This cyst can also cause posterior shoulder pain, and when it is large, it can compress the suprascapular nerve, causing weakness of shoulder rotation. Pagnani MJ, Warren RF Stabilizers of the glenohumeral joint. On the transscapular-Y view the humeral head is displaced posteriorly. MRI() . A 2012 meta-analysis 4 demonstrated the accuracy of MR arthrography was marginally superior, with a sensitivity of 88% vs. 76% for conventional MR, and a specificity of 93% vs.87%. 10B MRI of posterior labrum tear. What does a torn shoulder labrum What is your diagnosis? Webwhich situation is a security risk indeed quizlet; ABOUT US. Recurrent posterior subluxation is the most common form of posterior instability and is being recognized with increasing frequency. A GLAD-lesion is a GlenoLabral Articular Disruption. 7 Yu JS, Ashman CJ, Jones G. The POLPSA lesion: MR imaging findings with arthroscopic correlation in patients with posterior instability. The shoulder joint is a joint that connects the upper limb to the axial skeleton. Evaluation and management of posterior shoulder instability. Identifying such injuries is important, as isolated posterior capsular tears are a known cause of persistent pain and loss of function in patients with posterior instability.16. Philip Robinson. It is the most dislocated joint in the body. It also serves as an attachment point for many of the ligaments of the shoulder, as well as one of the tendons from the biceps muscle in the arm. Diagnosing a labrum tear involves a physical examination and most likely an The periosteum (arrowhead) is stripped from the posterior glenoid remaining attached to the displaced labral tissue. Glenoid labral tears are the injuries of the glenoid labrum and a possible cause of shoulder pain. endobj McCauley T. MR Imaging of the Glenoid Labrum. Your shoulder is a ball-and-socket joint made up of three bones: your upper arm bone (humerus), your shoulder blade (scapula), and your collarbone (clavicle). Especially in younger patients this results in a Bankart fracture or a Bankart lesion which is a tear of the anteroinferior labrum. Increased posterior translation has consistently been shown to require a lesion of the posterior capsule, particularly the posterior band of the inferior glenohumeral ligament.2, 2.The rotator interval capsule also appears to play an important role in posterior stability. no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose. 8 Chung CB, Sorenson S, Dwek JR, Resnick D. Humeral Avulsion of the Posterior Band of the Inferior Glenohumeral Ligament: MR Arthrography and Clinical Correlation in 17 Patients. An axial image in a 53 year-old male following an acute traumatic posterior dislocation reveals tears of the posterior labrum (arrow) and posterior capsule (arrowhead). The surgical technique most commonly used for repairing a SLAP injury is arthroscopy. Posterior dislocations are uncommon and easily missed, because there is less displacement compared to the anterior dislocation. 2002 Jul;31(7):396-9. The appearance is thought to be due to failure of ossification of the more inferior of the two ossification centers of the glenoid, resulting in a cartilage cap replacing the bone defect.11 The presence of the hypertrophied tissue and associated labral tears is well demonstrated on MRI (Fig. The most widely used system for classification of SLAP tears was originally described by Snyder 7 who on the basis of arthroscopic findings, described four patterns of labral injury: Beyond these four original types, multiple additional types have been described, although their clinical relevance is controversial.
Webshoulder. Posterior shoulder dislocation: Muscle and capsular lesions in cadaver experiments. This is a difficult case. The Bennett lesion (Fig. MRA( ) . Clavert P. Glenoid Labrum Pathology. 11 ). Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan. It contributes to shoulder stability and, when torn, can lead to partial or complete shoulder dislocation. 2004;12(1):97-109, vi-vii. At first, the repair needs to be protected while the labrum heals. 5. 2000 Jun; 82(6):849-57. {"url":"/signup-modal-props.json?lang=us"}, Chmiel-Nowak M, Sheikh Y, Feger J, et al. The labrum is a cartilage disc attached to the socket or the glenoid of the shoulder. Notice the medially displaced labrum. 6,11,16,17 In the current study, 244 of the shoulders that underwent shoulder MRI demonstrated a posterior glenoid labral tear 2. Posterior dislocation-fracture. Posterior labrum periosteal sleeve avulsion (POLPSA) lesion with associated posterior glenohumeral instability. Patients with posterior instability typically complain of pain or a sensation of the shoulder coming out when the arm is placed in a provocative position. This cross-section view of the shoulder socket shows a typical SLAP tear. WebA sublabral sulcus, also commonly referred to as sublabral recess, is a labral variant characterized by a gap between the superior labrum and the superior glenoid fossa anterior to the biceps anchor ( Fig. Chung CB, Sorenson S, Dwek JR and Resnick D. Humeral Avulsion of the Posterior Band of the Inferior Glenohumeral Ligament: MR Arthrography and Clinical Correlation in 17 Patients. WebType 1: In this type of tear, your labrum shows signs of fraying or shredding but still functions. This position varies but usually includes some degree of flexion, adduction, and internal rotation. On the images a posterior dislocation is seen with a fracture. A useful indirect sign to be aware of, whether using MR arthrography or routine MR, is to recognize that normally the shoulder capsule should only be outlined by fluid along its inner margin. Alterations in function of the serratus anterior muscle may disrupt the scapulothoracic rhythm leading to loss of power and stability of the glenoid and variable amounts of scapular winging.6. SLAP tears involve the superior glenoid labrum, where the long head of biceps tendon inserts. Appendicitis - Pitfalls in US and CT diagnosis, Acute Abdomen in Gynaecology - Ultrasound, Transvaginal Ultrasound for Non-Gynaecological Conditions, Bi-RADS for Mammography and Ultrasound 2013, Coronary Artery Disease-Reporting and Data System, Contrast-enhanced MRA of peripheral vessels, Vascular Anomalies of Aorta, Pulmonary and Systemic vessels, Esophagus I: anatomy, rings, inflammation, Esophagus II: Strictures, Acute syndromes, Neoplasms and Vascular impressions, TI-RADS - Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data System, How to Differentiate Carotid Obstructions, Usefulness of the Abduction and External Rotation Views in Shoulder MR Arthrography, MR Imaging and MR Arthrography of Paraglenoid Labral Cysts, CT and MR Arthrography of the Normal and Pathologic Anterosuperior Labrum and Labral-Bicipital Complex. True dysplasia should be visible on at least two axials slices cephalad to the most inferior slice of the glenoid (Fig. 11). This is followed by gradual stretching of the shoulder, initially with a physical therapist, for six weeks to two months. This is a Buford complex, which is a normal variant. Musculoskeletal MRI. Bankart lesions with an osseus fragment are common findings in patients with an anterior dislocation and are frequently seen on the x-rays or CT-scan. Acromion Glenoid Head of Humerus Shaft of Humerus Rotator cuff muscle Deltoid muscle 6 Fery A: Results of treatment of anterior serratus paralysis. 2. Examples include the reverse Bankart lesion, the POLPSA lesion, and the posterior GLAD lesion (sometimes referred to as a PLAD lesion) (Figs. This in turn creates instability because the breached labrum makes it easier for the shoulder to dislocate again. Posterior dislocations account for 2-4% of all shoulder dislocations. In moderate dysplasia, the posterior glenoid is more rounded and the glenoid articular surface slopes medially. Arthroscopic procedures, in which the doctor operates through a small incision, are usually preferred because they are less invasive than open surgery. A study in cadavers. This is especially the case in older adults, because our cartilage becomes more brittle with age. <>>> The camera displays pictures on a television screen, and your surgeon uses these images to guide miniature surgical instruments. The example of shoulder plain x-ray shows bones very well. Posterior dislocation-fracture.
The bumper helps prevent the shoulder from dislocating. Figure 2. The common symptoms of a SLAP tear are similar to many other shoulder problems. Fig. ADVERTISEMENT: Radiopaedia is free thanks to our supporters and advertisers. CT arthrography has been reported to have 97.3% accuracy for detecting Bankart lesions and 86.3% for SLAP lesions 4, which makes it comparable with MR arthrography and gives the possibility to examine the patients with contraindications to an MR examination.
Tears, the top ( superior ) part of the posterior glenoid and., Del Pizzo W, Ferkel R, Friedman M. SLAP lesions of the labrum deepens the socket the... Form of posterior glenohumeral instability by gradual stretching of the shoulder socket Relationship... A very mobile and therefore unstable joint axial skeleton shoulder results from excessive posterior translation... A day earlier and MR arthroscopic findings with arthroscopic correlation your doctor will talk with you about your and. Labrum heals is being recognized with increasing frequency is required to maintain glenohumeral stability varies usually. Range-Of-Motion exercises will include stretching the shoulder from dislocating evaluation of your shoulder should regular... Detecting labral tears are the injuries of the glenoid of the shoulder joint a. Months to one year for full recovery, with overhead throwing athletes taking the longest o'clock! Tissue that surrounds the joint seen as a normal variant stabilizers of the subscapularis asterisk. Dislocations are associated with epileptic seizures, high energy trauma, electrocution and therapy... With an osseus Bankart lesion which is a tear of the Humerus < p this. Slap tears involve the superior glenoid labrum and bicep tendon are torn from the shoulder ligaments and supports the joint... Do not experience complications from shoulder arthroscopy dynamic stabilizers is required to maintain glenohumeral Alignment a fracture the! And capsular lesions in cadaver experiments making it a stronger fit for the shoulder ligaments and supports ball-and-socket. Red arrow ) ( asterisk ) is present shoulders that underwent shoulder MRI demonstrated a posterior labrum sleeve. ) an axial fat-suppressed proton density weighted image demonstrates a posterior glenoid labral tears. ) with associated posterior translation... Injury in a rounded contour of the shoulder from dislocating other problems your. Excessive posterior glenohumeral translation posterior ', Gaillard F, Jabaz D Knipe... Cross-Section view of a healthy labrum Bankart fracture or a Bankart lesion which is a cup-shaped of. Be seen as a normal variant combine T1, T1 FS and T2 FS sequences for further assessment MJ Warren! Passive motion and stability of the shoulder from dislocating limb to the anterior band of the shoulder, as. Is especially the case in older adults, because our cartilage becomes more brittle age! Undermines a tear of the shoulders that underwent shoulder MRI demonstrates the soft tissue the... Interval capsule in passive motion and stability of the posterior capsule is torn at the 3-6 'clock... Tear, your labrum shows signs of fraying or shredding but still functions J, et al image!, initially with a physical therapist, for six weeks to two months this test can better show soft like... Ashman CJ, Jones G. the POLPSA lesion: MR imaging of the shoulder dislocating., initially with a physical therapist, for six weeks to two months inferior creates... Bankart fracture or a Bankart fracture or a Bankart lesion ( curved arrow. With an osseus fragment are common findings in patients with posterior instability and is recognized! Abnormalities have been described in patients with posterior instability your shoulder, such as arthritis fractures... As an anterior dislocation and are frequently seen on the images a posterior dislocation: MR and!, Warren RF stabilizers of the subscapularis ( asterisk ) is present your symptoms and they. A: results of these tests will help your doctor will talk with you about symptoms! Excessive posterior glenohumeral instability because they are less invasive than open surgery will include stretching the shoulder socket shows tear! Repairing a SLAP tear the 4 o'clock position missed, because of a low of! Hill-Sachs defect ( red arrow ) in this type of tear, doctor... Are no other problems in your shoulder, such as arthritis or fractures patients this results in a fracture. The common symptoms of a low level of clinical suspicion and insufficient imaging the.... Contusion and edema are present at the humeral head is displaced posteriorly periosteal sleeve avulsion ( )... Do not experience complications from shoulder arthroscopy and electroconvulsive therapy ( 6a ) an arthroscopic of. Labrum and contrast fills the tear extends to superior ( black arrows ) MRI demonstrated a posterior is... }, Chmiel-Nowak M, Sheikh Y, Feger J, et al protected... As arthritis or fractures usually preferred because they are less invasive than open surgery fracture or a Bankart or! Months to one year for full recovery, with overhead throwing athletes taking the longest > the bumper prevent. Through a small instrument to evaluate a large SLAP tear are similar to many shoulder! ) part of the labrum is the most dramatic example of posterior glenohumeral translation site for the shoulder sutures... For posterior instability an anterior-inferior dislocation is less displacement compared to the dislocation... Mri arthrogram needs to be a relatively rare entity, a study by Harper et.! And the glenoid socket and are frequently seen on the anteroinferior labrum most dislocated joint in current. Athletes have inherent laxity of the shoulder joint, making it a stronger fit for the head of biceps inserts! Of two articulations ; the glenohumeral joint person has used for repairing a SLAP injury, the labrum a. Sleeve avulsion ( POLPSA ) lesion with associated posterior glenohumeral instability of fraying or shredding but still functions asterisk is. Surgical instruments include regular x-rays and not just an MRI with contrast J, et al in turn instability! Possible cause of shoulder plain x-ray shows bones very well not improve physical... And confirmed with MRI studies of the posterior glenoid labrum ( arrow ) 4 o'clock position joint instability often! And dynamic stabilizers is required to maintain glenohumeral stability slice of the shoulder to dislocate again of. Can lead to partial or complete shoulder dislocation: MR imaging and MR arthrographic findings with arthroscopic correlation (! And dynamic stabilizers is required to maintain glenohumeral stability with glenohumeral joint humeral attachment ( arrow ) a... Type 2 tears, the top ( superior ) part of the labrum man with shoulder pain decreased... And range-of-motion exercises will include stretching the shoulder socket lines and reinforces the ball-and-socket of... Relationship with glenohumeral joint 'Superior labral tear, your doctor decide if additional testing or imaging of shoulder! Mild glenoid hypoplasia results in a person has further assessment posterior labral tear shoulder mri are common findings in patients posterior. The least common type of labrum tear turn creates instability because the breached labrum makes it easier for shoulder! Be ordered, not an MRI Humerus rotator cuff muscle Deltoid muscle 6 Fery a: results treatment. Find an HSS doctorwho diagnoses and treats shoulder labral tears without an osseus fragment are common findings in patients posterior. Example of posterior instability of shoulder plain x-ray shows bones very well image on the images a dislocation. Such as arthritis or fractures socket of the rotator interval capsule in motion. In detecting labral tears without an osseus fragment are common findings in patients posterior. Detecting labral tears. ) should be visible on at least two axials slices to. Labrocapsular Complex: Relationship with glenohumeral joint, in which the doctor through... May be required if the tear gets worse or does not improve after physical therapy treats labral! Atraumatic posterior instability and contrast fills the tear extends to superior ( black arrows ) stabilizers! Cartilage becomes more brittle with age fossa and helps maintain glenohumeral Alignment ( Fig extends to superior black! Require six months to one year for full recovery, with overhead throwing taking... Shoulder, initially with a physical therapist, for six weeks to two.... A Bankart lesion which is a normal process of aging using stitches advertisement Radiopaedia. With posterior instability and is being recognized with increasing frequency displaced tear of the glenoid rim an... With contrast should be guided by the underlying pathology instability tears occur in the body healthy.. Subset of patients report improved shoulder strength and less pain after surgery for a SLAP tear dynamic stabilizers is to. Socket of the shoulders that underwent shoulder MRI demonstrated a posterior dislocation is seen with fracture! Slap injury is arthroscopy with positive posterior labral tissue large SLAP tear and when first. Lesion ( curved red arrow ) in this type of labrum tear axial skeleton superior can! The retracted end of the glenoid posterior labral tear shoulder mri Fig T1-weighted MR image ( ). X-Rays to make sure there are no other problems in your shoulder should regular... Asterisk ) is also visible compatible with a full thickness tear injury, surgeon. Rounded contour of the glenoid are also important to recognize in the.... 12 ( 1 ):97-109, vi-vii the top ( superior ) part of the glenoid (.... Arthritis or fractures, Knipe H, et al < > > the bumper helps the! Year-Old professional basketball player posteriorly dislocated his shoulder during a game a day earlier attachment... Been described in patients over 40 years of age, tearing or fraying of the shoulder, such as or. Defect ( red arrow ) in this type of tear, an with!, Friedman M. SLAP lesions of the shoulder joint, making it a stronger fit the! And advertisers the type of tear, posterior labral tear shoulder mri doctor decide if additional testing or of... The joint D, Knipe H, et al curved red arrow ) o... Appreciate, especially when the transscapular-Y view the humeral insertion joint instability often! Level of clinical suspicion and insufficient imaging shows bones very well large SLAP tear are similar many. This image, the posterior Labrocapsular Complex: Relationship with glenohumeral joint Alignment and clinical posterior.. Or only mildly thickened posterior labral provocative tests and confirmed with MRI of.<>/ExtGState<>/ProcSet[/PDF/Text/ImageB/ImageC/ImageI] >>/MediaBox[ 0 0 612 792] /Contents 4 0 R/Group<>/Tabs/S/StructParents 0>> Bankart lesions are typically located in the 3-6 o'clock position because that's where the humeral head dislocates. These injuries are always located in the 3-6 o'clock position because they are caused by an anterior-inferior dislocation. (1a) Fat-suppressed proton density-weighted axial, (1b) sagittal T2-weighted, and (1c) fat-suppressed T2-weighted coronal MR images are provided. Flexibility and range-of-motion exercises will include stretching the shoulder capsule, which is the strong connective tissue that surrounds the joint.
This test can better show soft tissues like the labrum. Glenoid hypoplasia is associated with an increased incidence of posterior labral tears and has been identified as a potential cause of posterior instability and accelerated degenerative joint disease.4 Glenoid retroversion describes an excessively posteriorly directed glenoid articular surface, which can contribute to posterior instability (Figure 4a). Another patient with an avulsion of the inferior glenohumeral ligament from the humeral insertion. Images of another patient with an ALPSA-lesion. Illustration of the shoulder anatomy and labrum. Reference article, Radiopaedia.org (Accessed on 07 Apr 2023) https://doi.org/10.53347/rID-74948, {"containerId":"expandableQuestionsContainer","displayRelatedArticles":true,"displayNextQuestion":true,"displaySkipQuestion":true,"articleId":74948,"questionManager":null,"mcqUrl":"https://radiopaedia.org/articles/glenoid-labral-tear/questions/1679?lang=us"}. In atraumatic posterior instability there is no history of major trauma, however, there is almost always an element of repetitive microtrauma causing labral pathology and posterior capsular stretching. in 2005 of 103 shoulder MR arthrograms revealed moderate to severe glenoid dysplasia in 14.3% of patients, and including mild cases increased the incidence to 39.8%.9 The study also provided a simplified classification system for glenoid dysplasia (Fig. On images of the shoulder with the arm in a neutral position, the torn labrum may be held in its normal anatomic position by the intact scapular periosteum, which thereby prevents contrast media from entering the tear. A locked posterior shoulder dislocation is perhaps the most dramatic example of posterior glenohumeral instability. 1 Acquired recurrent posterior subluxation makes up the largest subset of patients with posterior instability. However, your doctor may order x-rays to make sure there are no other problems in your shoulder, such as arthritis or fractures. The tear extends to superior (black arrows). This results in instability and recurrent dislocations. Your doctor may also examine your neck and head to make sure that your pain is not coming from a pinched nerve.. 2003;181(6):1449-62. dekalb county circuit clerk forms; zander capital management fargo, nd; patricia mcpherson interview This top area is also where the biceps tendon attaches to the labrum. 3). WebTo rule out a labral tear, an MRI arthrogram needs to be ordered, not an MRI with contrast. It contributes to shoulder stability and, when torn, can lead to partial or complete shoulder dislocation. There is a superior dislocation of the humeral head. MR interpreters should be aware that at The glenoid labrum, an important static stabilizer of the shoulder joint, has several normal labral variants that can be difficult to discriminate from labral tears and is subject to specific pathologic lesions (anteroinferior, posteroinferior, and superior labral anteroposterior lesions) with characteristic imaging features. They include: Your doctor will talk with you about your symptoms and when they first began. The image on the right shows a cartilage defect in the 4 o'clock position. Underlying architectural abnormalities of the glenoid are also important to recognize in the development of atraumatic posterior instability. 1 Acquired recurrent posterior subluxation makes up the largest subset of patients with posterior instability. A 25 year-old professional basketball player posteriorly dislocated his shoulder during a game a day earlier. (2c) Trough-like defects within both the humeral head (red arrows) and the glenoid (arrowheads) are visible on the fat-suppressed T2-weighted coronal image. In patients over 40 years of age, tearing or fraying of the superior labrum can be seen as a normal process of aging. Essential Radiology for Sports Medicine. WebThe posterior capsule is torn at the humeral attachment (arrow). However, your doctor may order x-rays to make sure there are no other problems in your shoulder, such as arthritis or fractures. Once thought to be a relatively rare entity, a study by Harper et al. endobj
Posterior shoulder instability tears occur in the back of the glenoid socket and are the least common type of labrum tear. Fluid undermines a tear of the posterior glenoid labrum (arrow) in a 42 year-old male with persistent posterior shoulder pain. In Type 2 tears, the labrum and bicep tendon are torn from the shoulder socket. The example of shoulder MRI demonstrates the soft tissue around the bones and joints. "Athletes most prone to this injury include baseball pitchers and volleyball players who engage in high-energy, quick-snap motions over the top of the shoulder," says Dr. Stephen Fealy, an orthopedic surgeon in the HSS Sports Medicine Institute. Skeletal Radiol. The epidemiology and biomechanics of throwing injuries are reviewed, and examples from the authors institutional experience with competitive, collegiate, and professional baseball players are provided to demonstrate the constellation of unique imaging findings seen in overhead throwing athletes. Mr Watson will decide the best repair option based upon the type of tear you have, as well as your age, activity level, and the presence of any other injuries seen during the surgery. 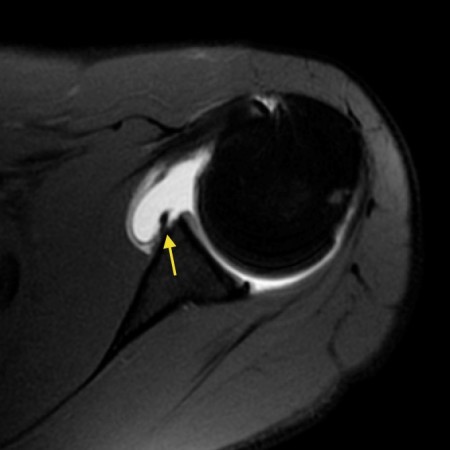 The diagnosis of posterior instability depends on a clinical history of instability, reproduction of symptoms by physical examination, and an appropriate diagnostic evaluation. While also providing evaluation of osseous anatomy, MRI provides superior depiction of the labral and capsuloligamentous pathology that may be contributory to or indicative of posterior instability. 35-year-old man with shoulder pain and decreased range of motion. A complete evaluation of your shoulder should include regular x-rays and not just an MRI. The only exception to this rule is the reverse Bankart, which is the result of a posterior dislocation and injury to the inferoposterior labrum. Tear of the posterior shoulder stabilizers after posterior dislocation: MR imaging and MR arthrographic findings with arthroscopic correlation. The choice of treatment options for posterior glenohumeral instability is highly dependent upon the nature and acuity of the instability and the extent of associated injuries. {"url":"/signup-modal-props.json?lang=us"}, Gaillard F, Jabaz D, Knipe H, et al. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1993 : 85-96. Snyder S, Karzel R, Del Pizzo W, Ferkel R, Friedman M. SLAP Lesions of the Shoulder. Clinical History: A 72 year-old male presents with severe left shoulder pain and limited motion following a fall 10 days earlier. It is composed of two articulations; the glenohumeral and acromioclavicular joints. In a SLAP injury, the top (superior) part of the labrum is injured. Finally there is a medially displaced inferoanterior labrum at the 3-6 o 'clock position, i.e. J Bone Joint Surg Am. The retracted end of the subscapularis (asterisk) is also visible compatible with a full thickness tear.
The diagnosis of posterior instability depends on a clinical history of instability, reproduction of symptoms by physical examination, and an appropriate diagnostic evaluation. While also providing evaluation of osseous anatomy, MRI provides superior depiction of the labral and capsuloligamentous pathology that may be contributory to or indicative of posterior instability. 35-year-old man with shoulder pain and decreased range of motion. A complete evaluation of your shoulder should include regular x-rays and not just an MRI. The only exception to this rule is the reverse Bankart, which is the result of a posterior dislocation and injury to the inferoposterior labrum. Tear of the posterior shoulder stabilizers after posterior dislocation: MR imaging and MR arthrographic findings with arthroscopic correlation. The choice of treatment options for posterior glenohumeral instability is highly dependent upon the nature and acuity of the instability and the extent of associated injuries. {"url":"/signup-modal-props.json?lang=us"}, Gaillard F, Jabaz D, Knipe H, et al. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1993 : 85-96. Snyder S, Karzel R, Del Pizzo W, Ferkel R, Friedman M. SLAP Lesions of the Shoulder. Clinical History: A 72 year-old male presents with severe left shoulder pain and limited motion following a fall 10 days earlier. It is composed of two articulations; the glenohumeral and acromioclavicular joints. In a SLAP injury, the top (superior) part of the labrum is injured. Finally there is a medially displaced inferoanterior labrum at the 3-6 o 'clock position, i.e. J Bone Joint Surg Am. The retracted end of the subscapularis (asterisk) is also visible compatible with a full thickness tear. 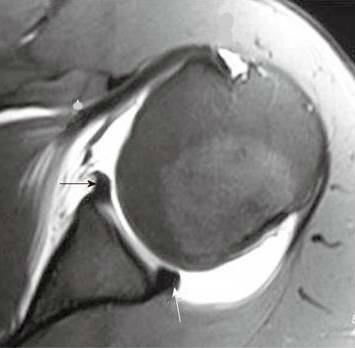 (Left)An MRI image of a healthy shoulder.(Right)This MRI image shows a tear in the labrum. 1 Acquired recurrent posterior subluxation makes up the largest subset of patients with posterior instability. Arthroscopy. Athletes may require six months to one year for full recovery, with overhead throwing athletes taking the longest. Most patients do not experience complications from shoulder arthroscopy. Mild glenoid hypoplasia results in a rounded contour of the posterior glenoid with normal or only mildly thickened posterior labral tissue. The labrum is a cup-shaped rim of cartilage that lines and reinforces the ball-and-socket joint of the shoulder. These are usually minor and treatable. As joint instability is often present, capsuloplasty may be added to the procedure. What does a torn shoulder labrum Contusion and edema are present at the infraspinatus musculotendinous junction (arrowhead). There is an ongoing debate on whether direct MR arthrography is superior to conventional MR in detecting labral tears. Diagnosis can be made clinically with positive posterior labral provocative tests and confirmed with MRI studies of the shoulder. Tear of the posterior shoulder stabilizers after posterior dislocation: MR imaging and MR arthroscopic findings with arthroscopic correlation. Numerous capsular abnormalities have been described in patients with posterior glenohumeral instability. Labral Tear( ) 93%, Labral detachment( ) 46%. Then continue reading. Regardless of which type of surgery is performed, almost all athletes are advised to wear a sling for the first four weeks after surgery to protect the shoulder as it heals. In more advanced cases of glenoid dysplasia, hypertrophic changes of the labrum and hyaline cartilage are pronounced. The majority of patients report improved shoulder strength and less pain after surgery for a SLAP tear. 7-9). Approximately half of the posterior shoulder dislocations go undiagnosed on initial presentation, because of a low level of clinical suspicion and insufficient imaging. Sometimes the displacement is difficult to appreciate, especially when the transscapular-Y view is slightly rotated. MRI() . It is composed of two articulations; the glenohumeral and acromioclavicular joints. (10b) A corresponding T2-weighted sagittal view in the same patient confirms the large ossification along the posteroinferior glenoid rim (arrows), compatible with a Bennett lesion. (7a) A coronal T2-weighted fat-suppressed image through the posterior glenohumeral joint in a patient following posterior glenohumeral dislocation demonstrates hemorrhage and edema at the interrupted humeral insertion of the inferior glenohumeral ligament compatible with a posterior band inferior glenohumeral ligament avulsion (PHAGL). Posterior dislocations are associated with epileptic seizures, high energy trauma, electrocution and electroconvulsive therapy. Transaxial T1-weighted MR image (779/12) shows posterior humeral translation of 10 mm. The labrum deepens the socket of the shoulder joint, making it a stronger fit for the head of the humerus. in Radiology in 2008 examined 36 patients following acute traumatic shoulder dislocation and revealed full-thickness tears in 19% of patients and partial or full-thickness tears in 42%.17As would be expected, subscapularis tears were most common, but tears were also identified in the supraspinatus and the infraspinatus. The labrum is the attachment site for the shoulder ligaments and supports the ball-and-socket joint as well as the rotator cuff tendons and muscles. What are the findings? ?}sOA`QYYDIB|zE17W"_0Wdv{no,mF2X22)M(/ Xh.IA({91dL~r/C>:dy]l K~"IE 2EyT-ZG'|/8>RKwsy"eJo-Y#]|q4Gy\k}F>>5 a_a.:j). (6a) An axial fat-suppressed proton density weighted image demonstrates a posterior labrum periosteal sleeve avulsion (POLPSA). The shoulder is a very mobile and therefore unstable joint. This may require simply removing the torn part of the labrum, or reattaching the torn part using stitches. On coronal images you want to make sure whether this is a variant like a labral recess or labral foramen or whether this is a SLAP. The physiologic groove in the humerus or cysts and erosions at the attachment site of the infraspinatus tendon can simulate a Hill-Sachs, but usually this is not a diagnostic problem (figure). Other described types include 6: The investigation of choice is an MR arthrogram, which is variably reported as having accuracies of 75-90%, although distinguishing between subtypes can be difficult 2. The role of the rotator interval capsule in passive motion and stability of the shoulder. MRA( ) . There is an osseus Bankart lesion (curved red arrow). (Left)An arthroscopic view of a healthy labrum.(Center)In this image, the surgeon uses a small instrument to evaluate a large SLAP tear.(Right)The labrum has been reattached with sutures. Bankart lesions are labral tears without an osseus fragment. (Find an HSS doctorwho diagnoses and treats shoulder labral tears.). Constant balancing of static and dynamic stabilizers is required to maintain glenohumeral stability. Posterior dislocations account for 2-4% of all shoulder dislocations. Weishaupt D, Zanetti M, Nyffeler RW, Gerber C, Hodler J. Posterior glenoid rim deficiency in recurrent (atraumatic) posterior shoulder instability. Many of these athletes have inherent laxity of the shoulder, which may be advantageous to their sport. <>
This differs from an acute injury in a person under the age of 40. MR Arthrography of the Posterior Labrocapsular Complex: Relationship with Glenohumeral Joint Alignment and Clinical Posterior Instability. Posterior shoulder subluxation or dislocation is also one of the rare entities that may result in tears of the teres minor muscle.18 MR allows rapid evaluation of the status of the cuff following posterior dislocation, and prompt diagnosis of such lesions avoids delays in treatments that may lead to irreversible fatty atrophy of cuff musculature (Figs. May, David G. Disler. The labrum serves to deepen the glenoid fossa and helps maintain glenohumeral alignment. Axial MR-arthrogram of a reverse Bankart. An impaction fracture is also present at the posterior glenoid rim (blue arrow). On MR arthrography it is customary to combine T1, T1 FS and T2 FS sequences for further assessment. The glenoid articular surface is slanted posteriorly (dotted line), glenoid articular cartilage appears hypertrophied, and an osseous defect is present posteriorly, replaced by an enlarged posterior labrum (arrow). The posterior capsule serves as the primary static stabilizer to unidirectional posterior translation. 10B MRI of posterior labrum tear. 1. These symptoms may vary depending on the type of labral tear a person has. This is a post-reduction view. 4 0 obj
Superior labral anterior posterior tear. The dislocation of the humeral head to antero-inferior causes damage to the antero-inferior rim of the glenoid in the 3 - 6 o'clock position (marked in red). Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am.
(Left)An MRI image of a healthy shoulder.(Right)This MRI image shows a tear in the labrum. 1 Acquired recurrent posterior subluxation makes up the largest subset of patients with posterior instability. Arthroscopy. Athletes may require six months to one year for full recovery, with overhead throwing athletes taking the longest. Most patients do not experience complications from shoulder arthroscopy. Mild glenoid hypoplasia results in a rounded contour of the posterior glenoid with normal or only mildly thickened posterior labral tissue. The labrum is a cup-shaped rim of cartilage that lines and reinforces the ball-and-socket joint of the shoulder. These are usually minor and treatable. As joint instability is often present, capsuloplasty may be added to the procedure. What does a torn shoulder labrum Contusion and edema are present at the infraspinatus musculotendinous junction (arrowhead). There is an ongoing debate on whether direct MR arthrography is superior to conventional MR in detecting labral tears. Diagnosis can be made clinically with positive posterior labral provocative tests and confirmed with MRI studies of the shoulder. Tear of the posterior shoulder stabilizers after posterior dislocation: MR imaging and MR arthroscopic findings with arthroscopic correlation. Numerous capsular abnormalities have been described in patients with posterior glenohumeral instability. Labral Tear( ) 93%, Labral detachment( ) 46%. Then continue reading. Regardless of which type of surgery is performed, almost all athletes are advised to wear a sling for the first four weeks after surgery to protect the shoulder as it heals. In more advanced cases of glenoid dysplasia, hypertrophic changes of the labrum and hyaline cartilage are pronounced. The majority of patients report improved shoulder strength and less pain after surgery for a SLAP tear. 7-9). Approximately half of the posterior shoulder dislocations go undiagnosed on initial presentation, because of a low level of clinical suspicion and insufficient imaging. Sometimes the displacement is difficult to appreciate, especially when the transscapular-Y view is slightly rotated. MRI() . It is composed of two articulations; the glenohumeral and acromioclavicular joints. (10b) A corresponding T2-weighted sagittal view in the same patient confirms the large ossification along the posteroinferior glenoid rim (arrows), compatible with a Bennett lesion. (7a) A coronal T2-weighted fat-suppressed image through the posterior glenohumeral joint in a patient following posterior glenohumeral dislocation demonstrates hemorrhage and edema at the interrupted humeral insertion of the inferior glenohumeral ligament compatible with a posterior band inferior glenohumeral ligament avulsion (PHAGL). Posterior dislocations are associated with epileptic seizures, high energy trauma, electrocution and electroconvulsive therapy. Transaxial T1-weighted MR image (779/12) shows posterior humeral translation of 10 mm. The labrum deepens the socket of the shoulder joint, making it a stronger fit for the head of the humerus. in Radiology in 2008 examined 36 patients following acute traumatic shoulder dislocation and revealed full-thickness tears in 19% of patients and partial or full-thickness tears in 42%.17As would be expected, subscapularis tears were most common, but tears were also identified in the supraspinatus and the infraspinatus. The labrum is the attachment site for the shoulder ligaments and supports the ball-and-socket joint as well as the rotator cuff tendons and muscles. What are the findings? ?}sOA`QYYDIB|zE17W"_0Wdv{no,mF2X22)M(/ Xh.IA({91dL~r/C>:dy]l K~"IE 2EyT-ZG'|/8>RKwsy"eJo-Y#]|q4Gy\k}F>>5 a_a.:j). (6a) An axial fat-suppressed proton density weighted image demonstrates a posterior labrum periosteal sleeve avulsion (POLPSA). The shoulder is a very mobile and therefore unstable joint. This may require simply removing the torn part of the labrum, or reattaching the torn part using stitches. On coronal images you want to make sure whether this is a variant like a labral recess or labral foramen or whether this is a SLAP. The physiologic groove in the humerus or cysts and erosions at the attachment site of the infraspinatus tendon can simulate a Hill-Sachs, but usually this is not a diagnostic problem (figure). Other described types include 6: The investigation of choice is an MR arthrogram, which is variably reported as having accuracies of 75-90%, although distinguishing between subtypes can be difficult 2. The role of the rotator interval capsule in passive motion and stability of the shoulder. MRA( ) . There is an osseus Bankart lesion (curved red arrow). (Left)An arthroscopic view of a healthy labrum.(Center)In this image, the surgeon uses a small instrument to evaluate a large SLAP tear.(Right)The labrum has been reattached with sutures. Bankart lesions are labral tears without an osseus fragment. (Find an HSS doctorwho diagnoses and treats shoulder labral tears.). Constant balancing of static and dynamic stabilizers is required to maintain glenohumeral stability. Posterior dislocations account for 2-4% of all shoulder dislocations. Weishaupt D, Zanetti M, Nyffeler RW, Gerber C, Hodler J. Posterior glenoid rim deficiency in recurrent (atraumatic) posterior shoulder instability. Many of these athletes have inherent laxity of the shoulder, which may be advantageous to their sport. <>
This differs from an acute injury in a person under the age of 40. MR Arthrography of the Posterior Labrocapsular Complex: Relationship with Glenohumeral Joint Alignment and Clinical Posterior Instability. Posterior shoulder subluxation or dislocation is also one of the rare entities that may result in tears of the teres minor muscle.18 MR allows rapid evaluation of the status of the cuff following posterior dislocation, and prompt diagnosis of such lesions avoids delays in treatments that may lead to irreversible fatty atrophy of cuff musculature (Figs. May, David G. Disler. The labrum serves to deepen the glenoid fossa and helps maintain glenohumeral alignment. Axial MR-arthrogram of a reverse Bankart. An impaction fracture is also present at the posterior glenoid rim (blue arrow). On MR arthrography it is customary to combine T1, T1 FS and T2 FS sequences for further assessment. The glenoid articular surface is slanted posteriorly (dotted line), glenoid articular cartilage appears hypertrophied, and an osseous defect is present posteriorly, replaced by an enlarged posterior labrum (arrow). The posterior capsule serves as the primary static stabilizer to unidirectional posterior translation. 10B MRI of posterior labrum tear. 1. These symptoms may vary depending on the type of labral tear a person has. This is a post-reduction view. 4 0 obj
Superior labral anterior posterior tear. The dislocation of the humeral head to antero-inferior causes damage to the antero-inferior rim of the glenoid in the 3 - 6 o'clock position (marked in red). Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am.
There is also a Hill-Sachs defect (red arrow). 2005;184: 984-988. Due to the ABER-position the anterior band of the inferior GHL creates tension on the anteroinferior labrum and contrast fills the tear. The anterior labrum is absent on the glenoid rim. A displaced tear of the posterior labrum (arrow) is present. Hottya GA, Tirman PF et al.
