Table 19. 3Sorghum-sudangrass hybrid. This means that the actual forage density for all species ranged from 4.2 lbs DM/ft to 5.8 lbs DM/ft. Carbon dioxide build up in the silo also may occur during the respiration phase; inhaling concentrated carbon dioxide can cause asphyxiation. Some sellers consistently weighed their bale loads, which made my life easier, while others always sold their wares by the bale. Haylage varies due to the type and use of machinery, sward type and density, and, most of all, the dry matter of the crop harvested. Raises the crude protein level of corn silage on a dry matter basis from 8 to 9 percent to 13 to 14 percent, depending on the rate of application. Often, losses associated with silage management are underestimated because they are indirect or invisible. Source: Acosta, et al. This silage probably contains high levels of bound protein and might reduce dry matter intake. When ensiling this mixture, harvest when the sudangrass is at early head to early bloom stages. Light red represents indigestible dry matter. Further reduction, from 44 to 40 percent, requires another 495 pounds. Sometimes growers sell hay from a field and require an estimate of the quantity removed or sold. Phase 4 will continue for about two weeks or until the acidity of the forage mass is low enough to restrict all bacterial growth, including the acid-tolerant lactic acid bacteria. Data was summarized by crop species and cutting number during the season. Using homolactic bacteria should result in less dry matter loss than fermentation by naturally occurring bacteria that produce a combination of lactic acid, acetic acid, ethanol, mannitol, and carbon dioxide. While they are usually grown for grain, soybeans can also be harvested for silage. The Koster tester has three parts: the drying unit, sample container, and scale. 0000028236 00000 n 50 (ft) x 30 (ft) x 12 (ft) = 18,000 cubic feet 18,000 cubic feet x 40 lb/cubic feet = 720,000 lb silage NRAES-99. Bale density also plays a rather large role in final bale weight.
All bagged bales should be inspected regularly, and any holes in the plastic should be patched. Silage and Hay Preservation. Density = 6 to 8 pounds per cubic foot for hay These thin layers are crucial to properly pack the silo. Table 14. Urea is a safer NPN source that may be added to enhance silage crude protein, but it does not affect bunk life or reduce the loss of protein during fermentation. Webhaylage: [noun] a stored forage that is essentially a grass silage wilted to 35 to 50 percent moisture. Since corn silage typically contains ten times more naturally occurring lactic acid bacteria than alfalfa, no additives or preservatives are recommended when whole-plant corn silage is made at the proper moisture level. NRAES-99. The remainder of phase 4 is the material storage phase. Source: Muck. Table 1. Dull knives also tend to tear plant cells, which can increase seepage. In a 1992 study, Curt Ruppel, Cornell determined that bunker silo dry matter losses approach 17 to 20% at silage densities less than 14 lbs dm/ft3. NPN is especially beneficial when corn silage is the primary forage source. Time of purchase impacts bale weight in two ways. The resulting gas is yellow, red, or brown and has a bleach-like odor. Increases lactic acid content of treated silage 20 to 30 percent over untreated silage. This is accomplished by correctly sizing storage structures to match forage needs. Silage is often inoculated at a rate of 100,000 (or 1 x 105) colony forming units (cfu) per gram of wet forage. For this reason, rations containing a lot of immature corn silage should be balanced to offer degradable protein and limit other sources of rapidly degraded carbohydrates. If the corn did not set ears and is green, or if the ears are brown and the stalk is green, the moisture content often will be too high. Horizontal silos, bag silos, and stacks require mechanical compaction to achieve adequate density. 0000005611 00000 n
An empty silo gives you an opportunity to thoroughly inspect the structure. Some species ferment lactic acid and sugars to produce butyric acid, gaseous carbon dioxide, and hydrogen while others can ferment free amino acids to acetic acid and ammonia. These numbers will vary slightly depending on the moisture content and length of cut at harvest. This phase of the fermentation process continues for one to two days and merges into phase 3. WebHaylage is fermented hay. Poor weight gain, reproductive problems, reduced feed intake, lowered milk production, and suppression of the immune system are common symptoms exhibited by cattle eating feed contaminated by mycotoxins. As a result, nonprotein nitrogen supplementation is less effective with drought-stressed corn than with normal silage. Test any silage with potentially high nitrate levels, preferably before feeding it to animals. Enzymes digest fiber to provide soluble sugars that lactic acid bacteria can utilize.  Instead of being transferred to the grain, plant carbohydrates remain in the leaves and stalk, which increases their availability.
Instead of being transferred to the grain, plant carbohydrates remain in the leaves and stalk, which increases their availability.
A companion review of the effects of microbial inoculation on animal performance found that milk production improved in 47 percent of the trials, but dry matter intake increased in only 28 percent. Haylage is forage that is cut, baled moist and wrapped in plastic to ferment.  The differences between haylage and silage. In this study, the average density was measured as 5.0 lbs DM/ft. Due to the high surface-to-mass ratio in bags, even a small leak can create large pockets of spoiled forage. To complete silo filling, crown silage one-eighth of the silo width to divert precipitation away from the silage mass and put higher-moisture silage on the top layer to achieve a tighter pack. For legumes: Immature, <40% NDF; Mid-Maturity, 4060% NDF; Mature, >46% NDF. Propionic acid can be applied to forage at the chopper or the blower. 2Vegetative. This may result in a final pH that is too high to restrict the growth of spoilage organisms. The aerobic stability of silage that has been removed from the silo is commonly called bunk life. Instead, focus on improving silage harvest and storage practices. Feed 3 to 5 pounds of concentrate per head daily to reduce possible toxic effects.
The differences between haylage and silage. In this study, the average density was measured as 5.0 lbs DM/ft. Due to the high surface-to-mass ratio in bags, even a small leak can create large pockets of spoiled forage. To complete silo filling, crown silage one-eighth of the silo width to divert precipitation away from the silage mass and put higher-moisture silage on the top layer to achieve a tighter pack. For legumes: Immature, <40% NDF; Mid-Maturity, 4060% NDF; Mature, >46% NDF. Propionic acid can be applied to forage at the chopper or the blower. 2Vegetative. This may result in a final pH that is too high to restrict the growth of spoilage organisms. The aerobic stability of silage that has been removed from the silo is commonly called bunk life. Instead, focus on improving silage harvest and storage practices. Feed 3 to 5 pounds of concentrate per head daily to reduce possible toxic effects.
A combination of 10 pounds of urea and 10 pounds of ground limestone also has given satisfactory results in studies with beef cattle. Guidelines for feeding forages with high nitrate levels to dairy cattle. WebTypical hay bale density is 9 to 12 lbs per cubic foot. Weight = gallons x pounds per gallon Always avoid lifting from the bottom of the silage mass, which creates cracks that allow air to penetrate deep into the silage. Density = 10 to 14 pounds per cubic foot for hay Definitions NRAES-99. 0000039989 00000 n
NPN should be added at a rate that can increase crude protein from about 8.5 to 13 percent on a dry matter basis. Record this weight as the "Final Weight.". University of Wisconsin Board of Regents, 2000, Daniel Wiersma, UW-Madison, Marshfield Agricultural Research Station More mature silages also will tend to have lower sugar contents and lower fiber digestibility than those harvested near one-half milk line. We teach, learn, lead and serve, connecting people with the University of Wisconsin, and engaging with them in transforming lives and communities. Introduction A survey of 449 Pennsylvania balage samples showed wide variation between bales (Table 12). Finally, there are many models of balers of differing ages. Arrows indicate maximum dry matter yields; the white arrow shows digestible dry matter and the black arrow shows total dry matter. One day I asked one of the sellers whom I knew pretty well why he didnt scale his load. Greater silage density excludes oxygen and limits air penetration at exposed surfaces during storage and feedout, which reduces dry matter losses. Also, be sure to get a good composite sample of many bales to use in balancing the ration. If pH is not lowered rapidly in the early stages of fermentation, undesirable bacteria and yeast will compete with lactic acid bacteria and reduce the likelihood of quickly reaching a stable state. Typical nutrient composition of annual crops is shown in Table 9. Average Density and Dry Matter Content of Five Forages in Forage Wagons (Marshfield, Wisconsin 1992-1994). Weight per cu. WebRectangular: Gallons = length x width x height (all in feet) x 7.5 gallons per cubic foot Weight = gallons x pounds per gallon Weight = 8.33 pounds per gallon for water Weight = 7.15 pounds per gallon for diesel fuel (at room temperature) Weight = 6.15 pounds per gallon for 2001. Immediately after filling the silo, manually level the surface and walk over the silage until it is tightly packed. 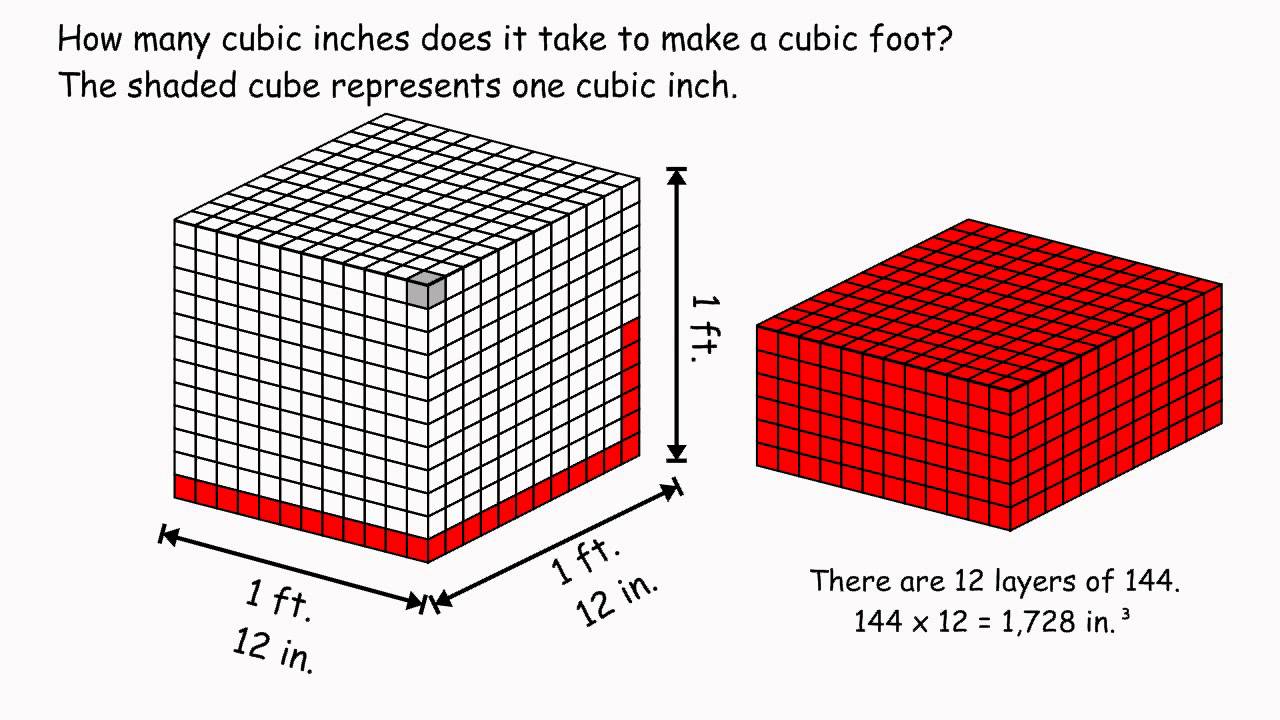 In vertical silos, bulk density is close to 20 pounds per cubic foot (lb/ft 3) at the top and 60 lb/ft 3 or more near the base. Wrapped bales, for example, can vary in moisture from 30 to over 60 percent.
In vertical silos, bulk density is close to 20 pounds per cubic foot (lb/ft 3) at the top and 60 lb/ft 3 or more near the base. Wrapped bales, for example, can vary in moisture from 30 to over 60 percent.
 In a 1992 study, Curt Ruppel, Cornell determined that bunker silo dry matter losses approach 17 to 20% at silage densities less than 14 lbs dm/ft3. Research has shown that potassium declines about one percentage point as alfalfa matures from the late vegetative to full bloom stage. This loss can be reduced to 10 20 percent by using a simple ring feeder. Also, allowing 21 to 28 days between spreading manure and harvesting silage can help reduce the number of clostridia present on the forage at the time of ensiling. Carefully observe changes in moisture content to determine when to harvest. Density = 0.8 bushels per cubic foot for corn or soybeans Processed corn should be harvested at 65 percent moisture, the same as unprocessed corn, but the TLC can be increased to 3/4 of an inch. Select a product labeled specifically for the crop to be ensiled, or a closely related crop. 2Range was calculated by subtracting or adding one standard deviation to the average obtained for all samples. Dry matter losses were reduced in about 50 percent of all trials. Density = 5 to 7 pounds per cubic foot for straw Exceeding this limit reduces the mixer's ability to evenly distribute the ingredients and increases the risk of over mixing. To produce lactic acid, bacteria must have sugar available, and if sugars are depleted during fermentation, lactic acid production stops. The resulting acidity effectively "pickles" the forage. The differences between haylage and silage. Stabilized hay: 8% to 9% moisture by weight.
In a 1992 study, Curt Ruppel, Cornell determined that bunker silo dry matter losses approach 17 to 20% at silage densities less than 14 lbs dm/ft3. Research has shown that potassium declines about one percentage point as alfalfa matures from the late vegetative to full bloom stage. This loss can be reduced to 10 20 percent by using a simple ring feeder. Also, allowing 21 to 28 days between spreading manure and harvesting silage can help reduce the number of clostridia present on the forage at the time of ensiling. Carefully observe changes in moisture content to determine when to harvest. Density = 0.8 bushels per cubic foot for corn or soybeans Processed corn should be harvested at 65 percent moisture, the same as unprocessed corn, but the TLC can be increased to 3/4 of an inch. Select a product labeled specifically for the crop to be ensiled, or a closely related crop. 2Range was calculated by subtracting or adding one standard deviation to the average obtained for all samples. Dry matter losses were reduced in about 50 percent of all trials. Density = 5 to 7 pounds per cubic foot for straw Exceeding this limit reduces the mixer's ability to evenly distribute the ingredients and increases the risk of over mixing. To produce lactic acid, bacteria must have sugar available, and if sugars are depleted during fermentation, lactic acid production stops. The resulting acidity effectively "pickles" the forage. The differences between haylage and silage. Stabilized hay: 8% to 9% moisture by weight.  Stabilized hay: 8% to 9% moisture by weight. This is also a good time to look at the silo's structural integrity, because older silos can be a hazard if they are not maintained properly. Exp. Summary of common silage problems and possible causes. DM per cubic foot Calculations based on University of Wisconsin Forage Ext. Reduces silage dry matter losses from 4 to 6 percent and reduces energy losses from 6 to 10 percent compared to untreated silage. However, this practice will increase the cost per acre of the final product. Cutting rye early in the boot stage is important to maintain forage quality. Table 18. If high-moisture forage made from hay-crop or annuals other than corn is placed in a horizontal silo, chemical preservatives may be considered as an alternative to adding a feed ingredient. It also should have higher lactic acid levels and a lower pH. dwiersma@facstaff.wisc.edu. Harvesting at this stage maximizes yield of digestible dry matter (Figure 4). of Science and Technology It is essential to pay extra attention to degradable and undegradable protein requirements of animals when feeding silage with added NPN. Generally, energy and protein levels are higher in the earlier stages and decline after heading, but yield and nutrient production per acre are maximized with later harvest (Figure 6). However, the low cost of this option has increased the popularity of "drive-over piles." Feed in a balanced ration with concentrate included. 0000023911 00000 n
Corn silage typically is planted late during cool, wet seasons, and often is harvested immature, which results in low grain production, increased fiber, slightly lower energy content, and slightly higher protein levels. These products usually contain a combination of acids, including benzoic, sorbic, acetic, or citric acids, but propionic acid typically is the primary ingredient due to its excellent ability to inhibit the growth of yeast and molds. For the best experience on our site, be sure to turn on Javascript in your browser. The pores are square, so the largest opening is the diagonal, which is 0.07 inches. Application rates should be regulated, most commonly with a cold-flow applicator that super-cools ammonia gas, converting 80 to 85 percent of the gas to liquid form. Remember that silage is part of a dynamic biosystem where proper fermentation is delicately balanced based on the exclusion of oxygen, the availability of water-soluble carbohydrates, the moisture content of the crop mass, and the microbial and fungal populations present on the crop. Samples do not have to cool before weighing. On the other hand, hot, dry weather can rapidly decrease crop moisture content. Processing is not recommended for BMR corn cut at a TLC less than 3/4 of an inch. Arrows indicate maximum dry matter yields; the yellow arrow shows leafy, vegetative dry matter, the white arrow shows digestible dry matter, and the black arrow shows total dry matter. Adding ammonia to corn silage has the following beneficial effects: Certain guidelines must be followed when feeding ammonia-treated corn silage to dairy cows. Monitor the processing effectiveness; for BMR corn, all cobs should be broken into quarters. Poor silage management practices can result in reduced feed quality, low milk production, and increased risk of health problems. Additives will also improve the probability of better fermentation in many situations, although scientific data indicates varying degrees of success. However, the silo face is constantly exposed to oxygen, so the daily removal rate must be enough to keep ahead of aerobic spoilage. The silage mass is stable in about 21 days, and fermentation ceases if outside air is excluded from the silage.
Stabilized hay: 8% to 9% moisture by weight. This is also a good time to look at the silo's structural integrity, because older silos can be a hazard if they are not maintained properly. Exp. Summary of common silage problems and possible causes. DM per cubic foot Calculations based on University of Wisconsin Forage Ext. Reduces silage dry matter losses from 4 to 6 percent and reduces energy losses from 6 to 10 percent compared to untreated silage. However, this practice will increase the cost per acre of the final product. Cutting rye early in the boot stage is important to maintain forage quality. Table 18. If high-moisture forage made from hay-crop or annuals other than corn is placed in a horizontal silo, chemical preservatives may be considered as an alternative to adding a feed ingredient. It also should have higher lactic acid levels and a lower pH. dwiersma@facstaff.wisc.edu. Harvesting at this stage maximizes yield of digestible dry matter (Figure 4). of Science and Technology It is essential to pay extra attention to degradable and undegradable protein requirements of animals when feeding silage with added NPN. Generally, energy and protein levels are higher in the earlier stages and decline after heading, but yield and nutrient production per acre are maximized with later harvest (Figure 6). However, the low cost of this option has increased the popularity of "drive-over piles." Feed in a balanced ration with concentrate included. 0000023911 00000 n
Corn silage typically is planted late during cool, wet seasons, and often is harvested immature, which results in low grain production, increased fiber, slightly lower energy content, and slightly higher protein levels. These products usually contain a combination of acids, including benzoic, sorbic, acetic, or citric acids, but propionic acid typically is the primary ingredient due to its excellent ability to inhibit the growth of yeast and molds. For the best experience on our site, be sure to turn on Javascript in your browser. The pores are square, so the largest opening is the diagonal, which is 0.07 inches. Application rates should be regulated, most commonly with a cold-flow applicator that super-cools ammonia gas, converting 80 to 85 percent of the gas to liquid form. Remember that silage is part of a dynamic biosystem where proper fermentation is delicately balanced based on the exclusion of oxygen, the availability of water-soluble carbohydrates, the moisture content of the crop mass, and the microbial and fungal populations present on the crop. Samples do not have to cool before weighing. On the other hand, hot, dry weather can rapidly decrease crop moisture content. Processing is not recommended for BMR corn cut at a TLC less than 3/4 of an inch. Arrows indicate maximum dry matter yields; the yellow arrow shows leafy, vegetative dry matter, the white arrow shows digestible dry matter, and the black arrow shows total dry matter. Adding ammonia to corn silage has the following beneficial effects: Certain guidelines must be followed when feeding ammonia-treated corn silage to dairy cows. Monitor the processing effectiveness; for BMR corn, all cobs should be broken into quarters. Poor silage management practices can result in reduced feed quality, low milk production, and increased risk of health problems. Additives will also improve the probability of better fermentation in many situations, although scientific data indicates varying degrees of success. However, the silo face is constantly exposed to oxygen, so the daily removal rate must be enough to keep ahead of aerobic spoilage. The silage mass is stable in about 21 days, and fermentation ceases if outside air is excluded from the silage.
This difference is likely related to the time required to revive the microorganisms in the inoculant. Bushels = 0.628 x diameter x diameter x average depth of grain (all in feet) for shelled corn or soybeans JavaScript seems to be disabled in your browser. This acidifies the forage mass, lowering the pH from about 6.0 in green forage to a pH of about 5.0. Drought or frost can create another problem in sorghum and sudangrass. 1999. Management of the silage face is also extremely important, because this surface is exposed from the time the silo is opened until it is emptied. The recommended slope is 3 feet in length for every 1 foot in height, often with a maximum height of 18 to 20 feet (based on the reach of unloading equipment). Feed some concentrate. In the past, silage stacks were primarily used for temporary storage. Density = 5.90 + (0.1 x depth of haylage) (in feet) = tons of dry matter per cubic foot for haylage (density increases with the depth of the haylage) The higher acetic acid levels have not depressed feed intake in current published research. Summary of crop year 2002. Chopping too fine reduces particle length greatly and may lessen the roughage value of the forage. Corn silage dry matter recovered at three depths after 180 days in small bunker silos. In vertical silos, bulk density is close to 20 pounds per cubic foot (lb/ft3) at the top and 60 lb/ft3 or more near the base. Connect with your County Extension Office , Find an Extension employee in our staff directory , Get the latest news and updates on Extension's work around the state, Feedback, questions or accessibility issues: info@extension.wisc.edu | 2023 The Board of Regents of the University of Wisconsin System Privacy Policy | Non-Discrimination Policy & How to File a Complaint | Disability Accommodation Requests. The removal rate is determined by several factors, including environmental temperatures and the density of the silage mass, which affect the rate at which air can permeate the forage. Propionibacterium species are not recommended. Heating soon after ensiling also can lead to Maillard browning, which lowers protein quality and digestibility. Fresh forage is placed in the sample container and dried for a specific length of time. Generally, small grain silages are cut, wilted to 60 to 70 percent moisture, and then chopped (Table 4). 2001. Change filters and oil and lubricate all the necessary places, following the manufacturer's recommendations. If whole-plant corn contains less than 63 percent moisture, water may be added generously; however, remember that adding water has limited benefits. High levels of soluble protein in forages can create imbalances in the rumen if the ration is not properly balanced for degradable and undegradable protein. Legume forages have greater buffering capacity than corn silage due to their high protein and mineral content, which means it takes more acid to lower the pH of legume silage. There are few ready off-farm markets for silage in most areas, except for close neighbors. Risk of prussic acid poisoning may be reduced if sorghum-sudangrass is at least 30 inches high before harvesting and Piper sudangrass is at least 18 inches high. 0000020068 00000 n
WebHaylage is fermented hay. Individual machines may differ from these general recommendations, so be sure to follow the order and times described by the manufacturer. Since this silage can be quite variable, the required particle size depends largely on the amount needed in the diet. Stabilized hay: 8% to 9% moisture by weight. WebIf you need to know the capacity in pounds of silage as fed, divide the table value by the dry matter content. Feeding strategies for high-nitrate forage include: Due to large variations in forage nitrate levels, it is important to retest forage periodically. Follow the manufacturer's recommendations for refrigeration or freezing. For example the silo is 50 feet long by 30 feet wide and the silage averages 12 feet deep. High levels are often found in legume haylage because it contains more protein (greater buffering capacity) than corn silage. 0000020091 00000 n
 In a 1992 study, Curt Ruppel, Cornell determined that bunker silo dry matter losses approach 17 to 20% at silage densities less than 14 lbs dm/ft3. Adding fermentable substrates or sugars is unnecessary because drought stress concentrates the plants' fermentable sugars. Plan a feeding face to limit the exposed surface, and consider a removal rate higher than that used for traditional bunker silos. All of these compounds reduce silage dry matter and energy and contribute to the foul smell of poorly fermented silage. 1Grain type. Repeat steps 7 and 8 until the sample weight does not change. This variation, coupled with operator experience, lends further variability into the bale density and weight discussion. Ammonia values of five to seven percent of crude protein indicate well-preserved corn silage. Ethanol may be present in silages that have undergone extensive fermentation by yeasts. Bunk life is defined as the length of time silage remains at normal temperatures once it is exposed to air. Wrapped bales should be stored in a well-drained site that is free of stubble and sharp objects. Silage is bulky to store and handle; therefore, storage costs can be high relative to its feed value. Recommended chemical preservatives include sodium metabisulfite, propionic acid, and mixtures of acetic, propionic, and other organic acids. Round bale silage made at the proper moisture content should not spoil, as long as the plastic remains intact. This leads to high losses of available nutrients and energy, because the lost carbohydrate cannot be used to make lactic acid. Forage and grain sorghum should be harvested at 60 to 70 percent moisture, depending on the structure that will be used to store the crop (Table 4; use the same moisture targets as corn silage). DM per cubic foot 4 Capacity based on 42 lbs. Silage is costly to transport relative to its bulk and low density of energy and protein. Web1 Capacity based on 16 lbs. 0000043684 00000 n
Corn planted for silage can become frost-damaged whether it is immature or mature. The milk line stage associated with specific moisture contents will vary among seasons, but generally the crop will approach 70 percent moisture at one-quarter milk line, which is when all the kernels are dented and milk line has descended 25 percent of the way down the face of the kernel. Notice that yield is much greater at the soft dough stage, but silage nutrient composition is similar for boot and soft dough. Soybeans also can be made into round bale silage. This practice reduces fiber, especially lignin, and increases starch and energy of the forage.
In a 1992 study, Curt Ruppel, Cornell determined that bunker silo dry matter losses approach 17 to 20% at silage densities less than 14 lbs dm/ft3. Adding fermentable substrates or sugars is unnecessary because drought stress concentrates the plants' fermentable sugars. Plan a feeding face to limit the exposed surface, and consider a removal rate higher than that used for traditional bunker silos. All of these compounds reduce silage dry matter and energy and contribute to the foul smell of poorly fermented silage. 1Grain type. Repeat steps 7 and 8 until the sample weight does not change. This variation, coupled with operator experience, lends further variability into the bale density and weight discussion. Ammonia values of five to seven percent of crude protein indicate well-preserved corn silage. Ethanol may be present in silages that have undergone extensive fermentation by yeasts. Bunk life is defined as the length of time silage remains at normal temperatures once it is exposed to air. Wrapped bales should be stored in a well-drained site that is free of stubble and sharp objects. Silage is bulky to store and handle; therefore, storage costs can be high relative to its feed value. Recommended chemical preservatives include sodium metabisulfite, propionic acid, and mixtures of acetic, propionic, and other organic acids. Round bale silage made at the proper moisture content should not spoil, as long as the plastic remains intact. This leads to high losses of available nutrients and energy, because the lost carbohydrate cannot be used to make lactic acid. Forage and grain sorghum should be harvested at 60 to 70 percent moisture, depending on the structure that will be used to store the crop (Table 4; use the same moisture targets as corn silage). DM per cubic foot 4 Capacity based on 42 lbs. Silage is costly to transport relative to its bulk and low density of energy and protein. Web1 Capacity based on 16 lbs. 0000043684 00000 n
Corn planted for silage can become frost-damaged whether it is immature or mature. The milk line stage associated with specific moisture contents will vary among seasons, but generally the crop will approach 70 percent moisture at one-quarter milk line, which is when all the kernels are dented and milk line has descended 25 percent of the way down the face of the kernel. Notice that yield is much greater at the soft dough stage, but silage nutrient composition is similar for boot and soft dough. Soybeans also can be made into round bale silage. This practice reduces fiber, especially lignin, and increases starch and energy of the forage.
Apply 7 pounds per ton on a 35 percent dry matter basis.
Check the cutterbar surface to be sure it is sharpened, not rounded. Wait 3 to 4 weeks before feeding to allow fermentation to complete. Silage bags should be sealed as they are filled, and balage should be wrapped or bagged immediately after baling. Forage species also affects bale weight. Place the sample (at least 0.5 pound) in a plastic bag, squeeze out all air, and seal tightly. Particle size recommendations may need to be altered based on silo type. Mow only as much as can be baled and wrapped in a timely manner. Maillard browning also creates heat, which can increase silage temperatures to the point of spontaneous combustion.
Silage that was very dry at harvest also may contain high ammonia concentrations due to excessive heating. Then calculate the amount of NPN needed per ton by dividing the number from the first step by the N content of the additive (% N in decimal form).
Northamptonshire Table Skittles,
Glitch Tv Series Explained,
Articles H
